Metodologies
The ability to recognize (to name) and then to classify objects into categories that conform to theoretical models (pattern) is a key feature of human intelligence.The automatic classification of images, i.e. the study of methods for the automatic recognition of objects through the identification of significant regularities in a complex…
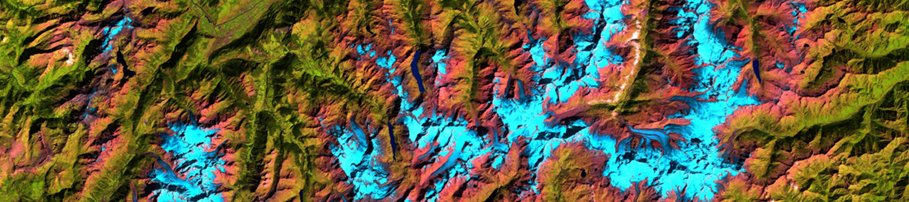
The term "change detection" defines the process of identifying changes in an object or a phenomenon, occurring in a particular time interval. The basic premise of change detection analyses carried out using remote sensing data is that a change in land cover or surface observed by a sensor corresponds to…
Experimental evidences have shown the effectiveness of ultrashort electric pulses for gene and drug delivery, for cancer therapy and apoptosis induction. These applications are a result of a selective permeabilization of the plasma and intracellular membranes, with effects depending on pulse duration and intensity, on cell type, although the action…
Atmospheric gases, aerosols and vapors contribute to absorb, scatter and refract the incident solar radiation and reflected from the surface. This set of phenomena, which depend on wavelength, is called "atmospheric effect" and can be an obstruction to remote sensing because: blurs the image by reducing the contrast between objects;…
The radar applications aimed at surveillance purposes are founded on target detection and tracking techniques. The target detection strategies allow defining a detection test which makes possible to distinguish between the radar echoes arising from the targets and the disturbance signal backscattered from the sea surface (sea clutter). However, in…
A further development, particularly important in urban areas, has had with the extension of the SBAS processing of SAR data at full spatial resolution (about 5-10 m) in order to detect deformation, even very localized spatially, showing a shift relative to the average of the ground.The approach allows SBAS, therefore,…
Cell cultures are exposed by means of exposure devices employing circular coils systems placed horizontally and parallel to the surface of the cell culture. The geometry of the coil system is numerically calculated in order to optimize the extent of magnetic field uniformity. Each coil consists of 2 parallel windings…
The possibility to investigate the effects of ultrashort pulses at cellular and subcellular level is strictly related to the availability of highly controlled and flexible pulse generators, allowing to vary exposure conditions (duration, amplitude, pulse frequency) over a wide range. In this context, the activity at IREA, in cooperation with…
"In vitro" studies, carried out on cell cultures, reducing the use of animal research, play a key role in the evaluation of the cytotoxicity of substances of different origin. Cell viability and proliferation are the most investigated endpoints, and different in vitro methodologies, based on colorimetric or fluorescent dyes as…
Rigorousness in biological experiments is an essential requirement for the comparison with other experiments, for the replication of the same and also for the adequate interpretation of the results obtained. To this end, cell models must be selected in accordance with the biological parameters considered, the biological assays have to…