Maria Consiglia Rasulo
Gloria Bordogna and Cristiano Fugazza of IREA-CNR announce the call of the Special Issue "Artificial Intelligence for Multisource Geospatial Information" of the International Journal of GeoInformation (IJGI), an international open-access peer-reviewed journal published by MDPI.
The Special Issue is devoted to collecting original research contributions focused on the definition and application of Artificial Intelligence methods for acquisition, filtering, management, analysis, discovery, and visualization of geospatial information from multiple sources, i.e., geospatial big data. Key applications are Earth observation for territorial monitoring and change detections, including urban and land use dynamics and anomaly detection; social conditions and habits detection, characterization, monitoring and prediction regarding, for example, poverty locations, citizens mobility, work, and recreation; event detection and forecasting for emergency preparedness and management, and many more. This field, also named geospatial artificial intelligence (or geoAI), applies many techniques of the most general artificial intelligence (AI), such as machine learning, deep learning, semantic representation and analysis, knowledge discovery, data mining, and soft computing. However, the specificities and importance of the geospatial dimension, its heterogeneity, the need for representing distinct semantics of locations, as well as to analyze the role of their temporal changes by performing geospatial and temporal reasoning pose new challenges and opportunities that AI has to face.
The deadline for submitting the articles is March 31st, 2020.
For all information go to this link.
 Brno, Czech Republic March 30-April 3, 2020
Brno, Czech Republic March 30-April 3, 2020
For further information, download the Call for Papers below
 What produced the recent Mount Etna volcanic-tectonic crisis, culminating with the ML 4.8 earthquake occurred along the Fiandaca Fault on the southeastern flank of the volcano? The main cause could be the ascent of deep magma, which could have put under tension the flanks of the volcano, triggering relevant seismic swarms along the Ragalna Fault System (southwest flank), the Pernicana Fault System (northeast flank) and, more violently, along the Fiandaca Fault (southeast flank), where the seismic swarm also produced a widespread surficial faulting and damage. The same ascent of deep magma could also have triggered the brief eruption of Mount Etna on 24-27 December 2018; the entire intrusive and deformative process may not have been completely exhausted (Figure 1 on the left).
What produced the recent Mount Etna volcanic-tectonic crisis, culminating with the ML 4.8 earthquake occurred along the Fiandaca Fault on the southeastern flank of the volcano? The main cause could be the ascent of deep magma, which could have put under tension the flanks of the volcano, triggering relevant seismic swarms along the Ragalna Fault System (southwest flank), the Pernicana Fault System (northeast flank) and, more violently, along the Fiandaca Fault (southeast flank), where the seismic swarm also produced a widespread surficial faulting and damage. The same ascent of deep magma could also have triggered the brief eruption of Mount Etna on 24-27 December 2018; the entire intrusive and deformative process may not have been completely exhausted (Figure 1 on the left).
This hypothesis is formulated in a study conducted by a team of researchers from the Institute for Electromagnetic Sensing of the Environment of the National Research Council (IREA-CNR, Naples) and the National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology (INGV, Catania and Rome), in collaboration with the Department of Civil Protection (DPC, Rome).
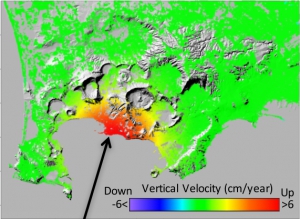
The results of this research are based on the analysis of the radar images of the Sentinel-1 satellites belonging to the constellation of the Copernicus European program, processed through the interferometric technique (InSAR), with which the Mount Etna ground deformations induced by the eruptive and seismic activity were measured with centimetre accuracy. "The availability of satellite radar data of the Sentinel-1 constellation, from the Copernicus European program, and of the COSMO-SkyMed constellation of the Italian Space Agency (ASI) and the Ministry of Defense", highlights Riccardo Lanari, director of IREA-CNR, "has allowed detecting in detail the ground movements that affected the Mount Etna volcanic edifice during the 24-27 December 2018 eruption. The identification of both magmatic and seismogenic sources, which caused the deformations detected by satellites, has been possible thanks to a multidisciplinary approach, which integrated the seismological and field data with the satellite radar data processed by IREA-CNR " (Figure 2).
Through a process called "data inversion" and with the help of mathematical models, the volcanic and seismic sources that generated the deformations were reconstructed, succeeding in demonstrating the causal link between eruption and earthquakes. "The analytical modeling", says Vincenzo De Novellis, IREA-CNR researcher "has allowed us to distinguish two different deformative sources connected with the magma intrusion: a very surficial one, which caused the opening of the observed cracks from which the lava has flown, and a deeper one (from 3 to 8.5 km) which exercised a tension on the volcano flanks, triggering the fault movement and, therefore, generating the numerous earthquakes recorded by the monitoring network of the INGV ” (Figure 3).
"That the strong subsidence of the area close to La Montagnola (about 3 km south of the Mount Etna summit crater area) was a secondary effect of the deep magmatic intrusion was only understood thanks to the analytical modeling" adds Simone Atzori, INGV researcher. "With the same technique," continues Atzori, "we have analyzed and quantified the interactions that occurred between the magma ascent and the surrounding faults, including the Fiandaca, Pernicana and Ragalna structures".
"Understanding the cause-effect relationships between magmatic intrusions and earthquakes has always been an extremely interesting scientific challenge, first of all for the implications that these studies have on the evaluation of seismic and volcanic hazard", concludes Marco Neri, senior researcher at INGV. "And it is not said that it is effectively concluded. By comparing the large ground deformations occurred in the last few months and the small eruption of December, we can suppose that the volcano still has energy to spend. These are important assessments, especially for a densely urbanized area such as the Mount Etna one, where almost a million people live in close contact with one of the most active volcanoes in the world”.
The results of this research, entitled "DInSAR analysis and analytical modeling of Mt. Etna displacements: the December 2018 volcano-tectonic crisis", have just been published on the American journal Geophysical Research Letters (https://doi.org/10.1029/2019GL082467) and are now available to the scientific community and Civil Protection, which has also contributed to the publication: these results will represent a reference point to improve risk estimation in an area with such a high population density.
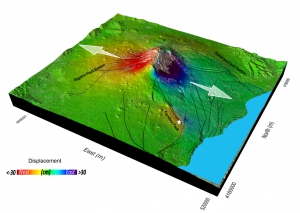
Figure 1. Above: Three-dimensional view of Mount Etna showing the eruptive fissures (white lines) from which the lava (in red) has flown on 24 December 2018, the main structural features of the volcano (black lines) and the 26 December earthquake (white star). The grey circles represent the epicentres of the earthquakes that nucleated from 24 to 27 December. Bottom: photograph acquired during a helicopter flight from west to east, in which it is possible to recognize the eruptive fissures (white dashed lines) and the main lava flow emerging from the cracks (red arrows). SEC: Southeast Crater; NSEC: New Southeast Crater; NEC: Northeast Crater.
See the presentation of the results to this link

Maria Rosaria Scarfì, a senior researcher of IREA-CNR, was appointed co-director of the International School of Bioelectromagnetics "Alessandro Chiabrera", one of the Schools of the Ettore Majorana Foundation and Center for Scientific Culture (EMFCSC) in Erice (Sicily). From 2003, the year of its establishment, the director was Ferdinando Bersani, professor of Physics at the University of Bologna.
The School proposes every two years a course, organized by two co-directors with recognized experience on the specific topic and by the School co-directors, aimed at young researchers and biologists, engineers and physicists, on different aspects of the interaction between nonionizing radiations and biological systems.
The Ettore Majorana Foundation and Center for Scientific Culture (EMFCSC) is a scientific organization, founded in 1962 by the physicist Antonino Zichichi, who is also its president, and named after the Sicilian physicist Ettore Majorana. Since its establishment in 1962, more than 120,000 scientists - of which many Nobel prizes - from 140 countries have taken part in post-university activities to promote science without secrets and without borders.
Monitoring crustal deformation in active volcanic areas could not be an easy task. Space-borne remote sensing can make the difference with respect to in-situ techniques, due to its capability to provide dense measurements at large spatial scale and at relatively low cost. These results will be presented on April 9th during a scientific talk (Room M2 at 9:30) and a press conference (at 13:00) at the next European Geophysical Union (EGU) General Assembly that will be held from 7th to 12th April in Vienna.
Differential Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry (DInSAR) is becoming one of the usual techniques to measure ground deformation with high accuracy and in any atmospheric conditions. The increasing diffusion of the use of DInSAR is due to the recent availability of huge and easily accessible SAR data archives, as those provided, since late 2014, by the Copernicus Sentinel-1 constellation. Sentinel-1 is nowadays providing SAR data every 6 days (in the best case) all over the Earth. It is therefore clear that with such a huge, global, constant and reliable availability of data it is possible to use the DInSAR technique for monitoring purposes, such as those related to the measurements of the ground motion in volcanic areas.
Researchers at the Institute of Electromagnetic Sensing of Environment (IREA) of the Italian National Research Council (CNR) have developed an operative service for monitoring the crustal deformation in active volcanoes through the use of DInSAR technique and Sentinel-1 data. The designed system is fully automatic and the process is triggered by the availability, for every monitored volcano site, of a new acquired Sentinel-1 data. The satellite data are ingested and processed through the well-known Parallel Small BAseline Subset (P-SBAS) DInSAR technique (fully developed at IREA-CNR) in order to generate the displacement time series of the investigated area.
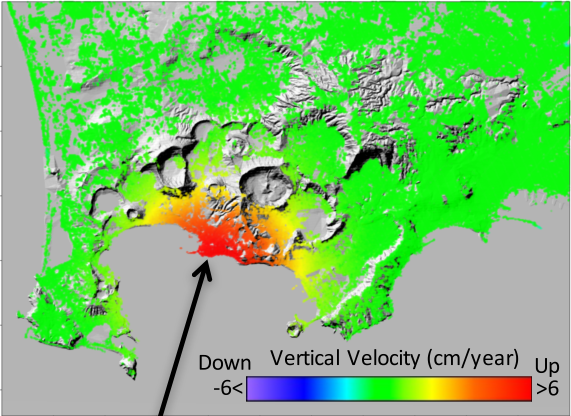
Being a Center of Competence (CoC) of the Italian Department of Civil Protection (DPC), CNR-IREA operates the described service to monitor the ground deformation of the main active Italian volcanoes, such as the Campi Flegrei caldera, Mt. Vesuvius, Ischia, Mt. Etna and Stromboli and provides monthly updates on the volcanoes’ deformation statuses to DPC and others CdC devoted to volcano monitoring. As an example, in the figure is reported the ground deformation affecting the Campi Flegrei caldera, near the city of Naples (Italy), which is experiencing an uplift of about 8.5 cm/year since July 2017.
Although the service is intended to serve the Italian DPC, it has been built to be easily portable and replicable for other volcanoes in the Earth, thus fully benefiting from the DInSAR monitoring capabilities of Sentinel-1.
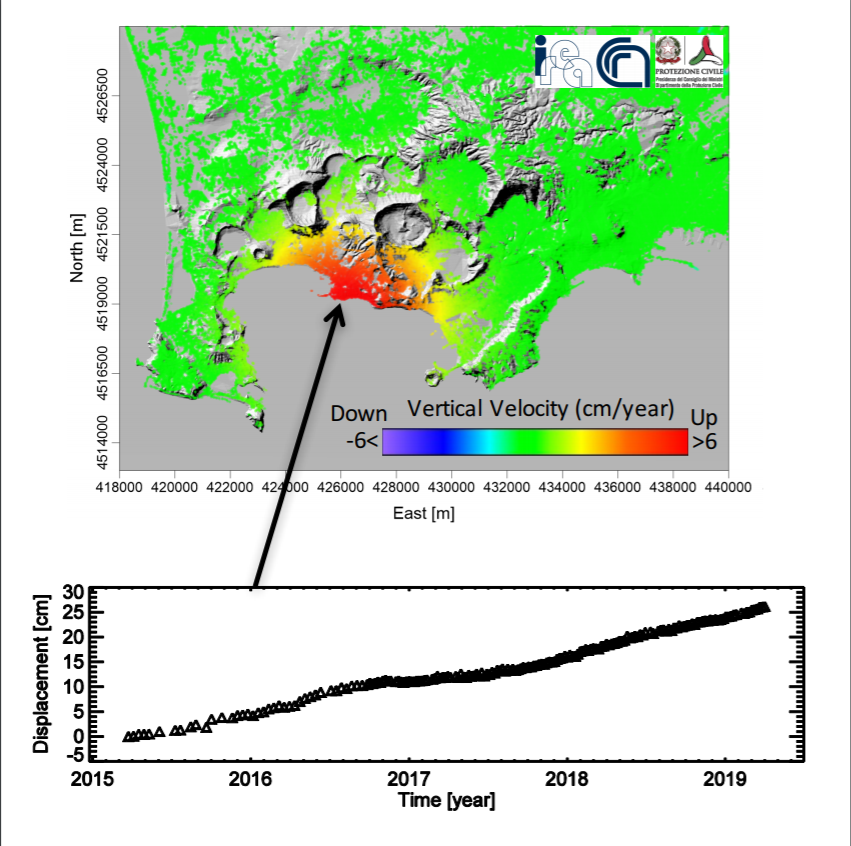
The graph shows the temporal evolution of the deformation that, since March 2015, uplifted of about 25 cm. Contains modified Copernicus data ©2019.
This work is supported by the IREA-CNR and Italian Civil Protection Department 2019-2021 agreement, the H2020 EPOS-IP project (GA 676564), the I-AMICA (PONa3_00363) project, and the IREA-CNR/DGS-UNMIG agreement.
 IREA, the Institute for Electromagnetic Sensing of the Environment of the National Research Council (CNR) of Italy, has selected ONDA, through a public invitation to tender open to the DIAS platforms, to provide cloud resources for processing Sentinel-1 data.
IREA, the Institute for Electromagnetic Sensing of the Environment of the National Research Council (CNR) of Italy, has selected ONDA, through a public invitation to tender open to the DIAS platforms, to provide cloud resources for processing Sentinel-1 data.
IREA has already been using the ONDA platform as an early adopter for the development of surface deformation products implementing interferometric SAR (InSAR) techniques.
“We are very pleased to continue our collaboration with ONDA,” said Riccardo Lanari, the IREA director. “We believe that the flexibility and reliability of the ONDA platform will be a benefit for us, especially as regards our developments on large scale InSAR data processing.
Indeed, these characteristics can be particularly relevant for our activities, carried out to support the Civil Protection Department of Italy and the Satellite Data Thematic Core Service of the European Plate Observing System (EPOS), which is the European Research Infrastructure Consortium (ERIC) focused on Solid Earth.”
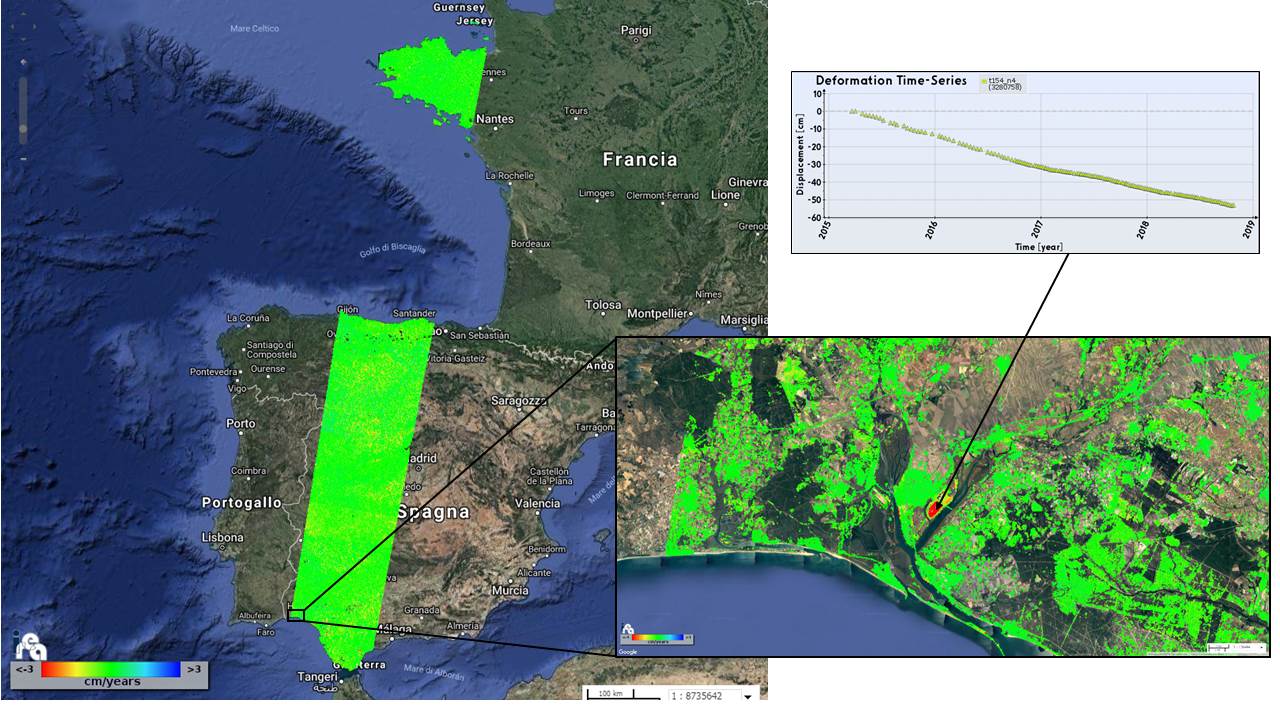
The figure above is an example of the products processed by IREA through the ONDA cloud resources, and shows the results related to the generated mean deformation velocity maps and the corresponding time series of 7 slices of the descending Sentinel-1 track no. 154.
Note that a large area of Spain is mapped through the first 6 slices, while the 7th one covers Normandy. To give an idea of the information content of the generated products, a zoom of a selected area (showing a localized deformation pattern) is also presented, as well as the retrieved deformation time series of one pixel.
The mapped area extends for almost 150000 km2 and for each slice a number of Sentinel-1 images ranging from 142 to 160 were processed.
Learn more:
• IREA Earth surface deformation project on ONDA Marketplace
• IREA (Institute for Electromagnetic Sensing of the Environment)
• CNR (National Research Council)
• Civil Protection Department (Italy)
• European Plate Observing System (EPOS)
• European Research Infrastructure Consortium (ERIC)
 For the past 34th years, the ACM Symposium on Applied Computing (SAC) has been a primary and international forum for applied computer scientists, computer engineers and application developers to gather, interact and present their work.
For the past 34th years, the ACM Symposium on Applied Computing (SAC) has been a primary and international forum for applied computer scientists, computer engineers and application developers to gather, interact and present their work.
The Information Access and Retrieval special track is concerned with the theory, implementation and evaluation of information access technologies to novel application areas and novel contexts.
Deadline for submission of regular papers and SRC research abstracts: Sept 10, 2018
For further information, download the Call for Papers
 The International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health (IJERPH) - ISSN 1660-4601, Impact Factor 2.145 - covers all the aspects of the environmental sciences, public health, occupational hygiene, and health-related research, in general. The Italian Society of Environmental Medicine (SIMA) is affiliated with IJERPH.
The International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health (IJERPH) - ISSN 1660-4601, Impact Factor 2.145 - covers all the aspects of the environmental sciences, public health, occupational hygiene, and health-related research, in general. The Italian Society of Environmental Medicine (SIMA) is affiliated with IJERPH.
This special issue, for which Maria Rosaria Scarfì and Olga Zeni are among the Guest Editors, is devoted to experimental, in vitro, in vivo and epidemiological studies, dealing with exposure to electric, magnetic and electromagnetic fields. The focus is on both possible adverse health effects and the beneficial effects, including biomedical applications, with particular attention to interaction mechanisms for the purposes of therapeutic and diagnostic applications.
More details are available at http://www.mdpi.com/journal/ijerph/special_issues/EMEFBM
Deadline for manuscript submissions: February 28, 2019
Within the Marie Skłodowska-Curie Innovative Training Network (MSCA-ITN) EMERALD, funded by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Programme, thirteen positions are available on fixed-term contracts for 36 months with a start date in either October 2018 or January 2019, depending on the host institution.
EMERALD (ElectroMagnetic imaging for a novel genERation of medicAL Device) is the coherent action of leading European engineering groups involved in electromagnetic (EM) technology for medical imaging to form a cohort of highly-skilled researchers capable of accelerating the translation of this technology “from the research bench to patient bedside”. To this end, EMERALD will establish a group of 13 outstanding early stage researchers who will be the European leaders in this field, through a unique scientific and training programme.
The EMERALD consortium involves academic institutions, industrial partners, hospitals and university medical centers. The EMERALD trained researchers will drive the future developments of EM imaging technology, thanks to the targeted skills they will attain, and their established connections with clinicians and stakeholders.
The specific calls are available on Euraxxes at the link: https://euraxess.ec.europa.eu/site/search?keywords=emerald
The deadline is June 1, 2018.
In particular, two positions are available at CNR-IREA in Naples:
The first one involves the development of Microwave Imaging algorithms for clinical follow-up devices. The main research topic will be the design, implementation, and testing of microwave imaging tools to process data collected by means of devices developed within the EMERALD network for clinical follow-up and image-guided treatment (e.g. chemotherapy follow-up, hyperthermia monitoring, image-guided thermal ablation).
The main research topic of the second position will be the design, realization, and testing of a non-invasive, safe, portable and cost-efficient microwave imaging device to monitor thermal ablation treatments.
For further information please contact Dr. Lorenzo Crocco ( This e-mail address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it )